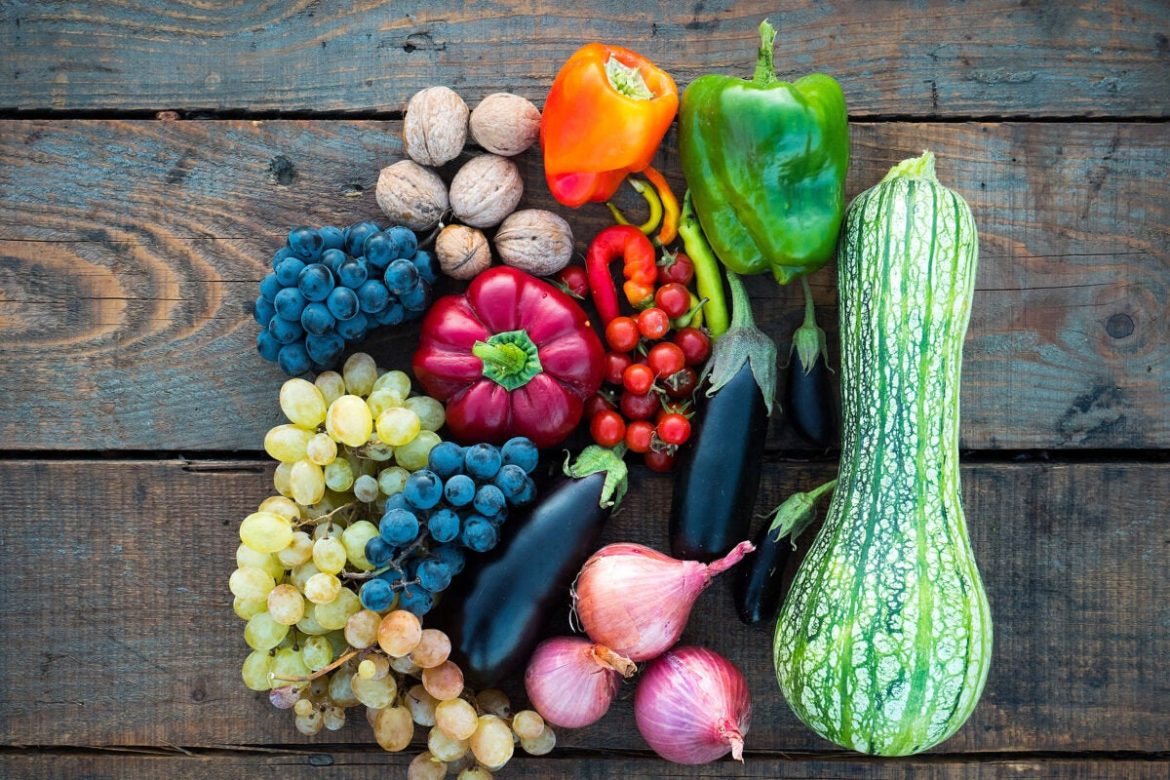
Although metabolic conditions such as obesity and Type 2 diabetes have been linked to an increased risk of COVID-19, as well as an increased risk of experiencing serious symptoms once infected, the impact of diet on these risks is unknown. In a recent study led by researchers at Harvard-affiliated Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and published in Gut, people whose diets were based on healthy plant-based foods had lower risks on both counts. The beneficial effects of diet on COVID-19 risk seemed especially relevant in individuals living in areas of high socioeconomic deprivation.
“Previous reports suggest that poor nutrition is a common feature among groups disproportionately affected by the pandemic, but data on the association between diet and COVID-19 risk and severity are lacking,” says lead author Jordi Merino, a research associate at the Diabetes Unit and Center for Genomic Medicine at MGH and an instructor in medicine at Harvard Medical School.
For the study, Merino and his colleagues examined data on 592,571 participants of the smartphone-based COVID-19 Symptom Study. Participants lived in the U.K. and the U.S., and they were recruited from March 24, 2020 and followed until Dec. 2, 2020. At the start of the study, participants completed a questionnaire that asked about their dietary habits before the pandemic. Diet quality was assessed using a healthful Plant-Based Diet Score that emphasizes healthy plant foods such as fruits and vegetables.
During follow-up, 31,831 participants developed COVID-19. Compared with individuals in the lowest quartile of the diet score, those in the highest quartile had a 9 percent lower risk of developing COVID-19 and a 41 percent lower risk of developing severe COVID-19. “These findings were consistent across a range of sensitivity analysis accounting for other healthy behaviors, social determinants of health and community virus transmission rates,” says Merino.
“Although we cannot emphasize enough the importance of getting vaccinated and wearing a mask in crowded indoor settings, our study suggests that individuals can also potentially reduce their risk of getting COVID-19 or having poor outcomes by paying attention to their diet,” says co-senior author Andrew Chan, a gastroenterologist and chief of the Clinical and Translational Epidemiology Unit at MGH.
The researchers also found a synergistic relationship between poor diet and increased socioeconomic deprivation with COVID-19 risk that was higher than the sum of the risk associated with each factor alone.
“Our models estimate that nearly a third of COVID-19 cases would have been prevented if one of two exposures — diet or deprivation — were not present,” says Merino.
The results also suggest that public health strategies that improve access to healthy foods and address social determinants of health may help to reduce the burden of the COVID-19 pandemic.
“Our findings are a call to governments and stakeholders to prioritize healthy diets and wellbeing with impactful policies, otherwise we risk losing decades of economic progress and a substantial increase in health disparities,” says Merino.
The study was co-led by investigators at Kings College London. Co-authors include Amit D. Joshi, Long H. Nguyen, Emily R. Leeming, Mohsen Mazidi, David A. Drew, Rachel Gibson, Mark S. Graham, Chun-Han Lo, Joan Capdevila, Benjamin Murray, Christina Hu, Somesh Selvachandran, Alexander Hammers, Shilpa N. Bhupathiraju, Shreela V. Sharma, Carole Sudre, Christina M. Astley, Jorge E. Chavarro, Sohee Kwon, Wenjie Ma, Cristina Menni, Walter C. Willett, Sebastien Ourselin, Claire J. Steves, Jonathan Wolf, Paul W. Franks, Timothy D. Spector, Sarah Berry, and Andrew T. Chan.
Funding for the study was provided by the National Institutes of Health, the National Institute for Health Research, the U.K. Medical Research Council/Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council, the Wellcome Trust, the Massachusetts Consortium on Pathogen Readiness, the American Gastroenterological Association, the American Diabetes Association, the Alzheimer’s Society and Zoe Ltd.